Overview
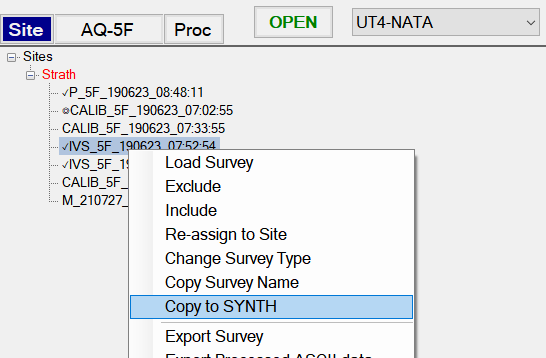
Synthetic seeding must be performed in a SYNTH survey type. When a SYNTH survey is collected it is typically an acquisition of the background which serves as a noise base for the seeding. If a SYNTH survey has not been collected yet, the user can copy an existing survey to a SYNTH survey type. For example an IVS survey from the UT4-NATA Classifier system can be selected and the user can Copy to SYNTH as shown below:
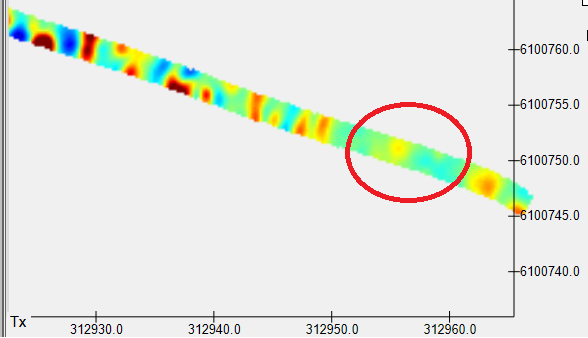
After we open the SYNTH survey, we could decide to set a synthetic seed in the area of the red circle (for example):
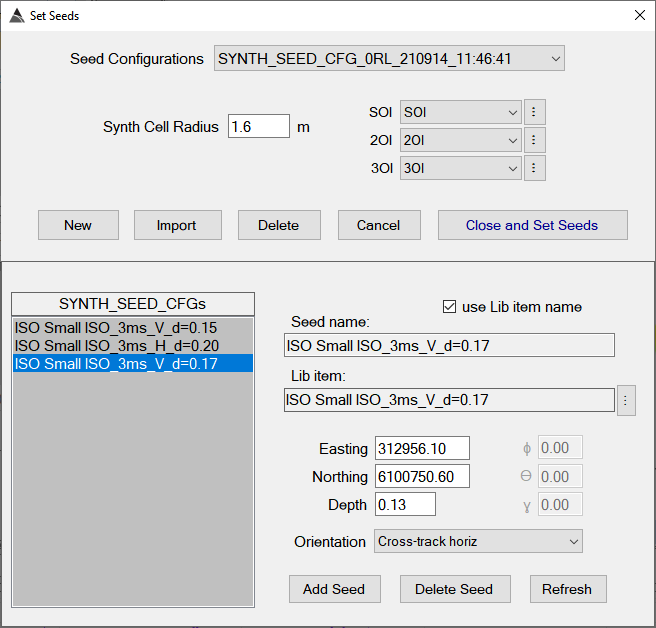
To get started, go to the MQO tab and ensure you have a Library configured and enabled first. After that, click on the “Set Seeds” button:
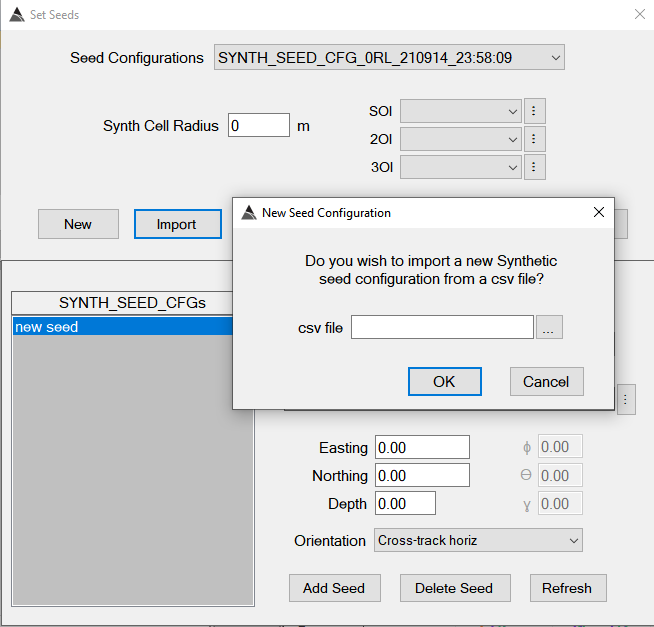
Create a new Synthetic Seed configuration using the New button, or the Import button if you have your seeds defined in a csv file. We will import from csv in this example.
Click on the Import button as shown here:
The csv file should have the following format (a header row is not required). The exact library item names should be specified. In this example, we have set three sources close to each other because we want to generate a multi-source scenario. Note that the seed items only require an integer value specifying the seeded orientation:
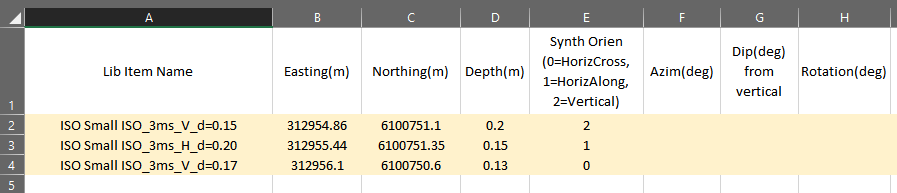
Once the seed configuration is imported, a Synth Cell Radius can be set, indicating the footprint of the synthetic data. BTField will automatically generate synthetic data for one, two or three sources, depending on how many items are clustered within the specified SYNTH cell area. In our example we will set a radius of 1.6m, therefore all three of our seed items will be used to generate a three source synthetic seeding.
Also note that after import, the seed configuration can be modified. For example, if any of the CSV library items cannot be automatically found, they can be manually selected after the import.
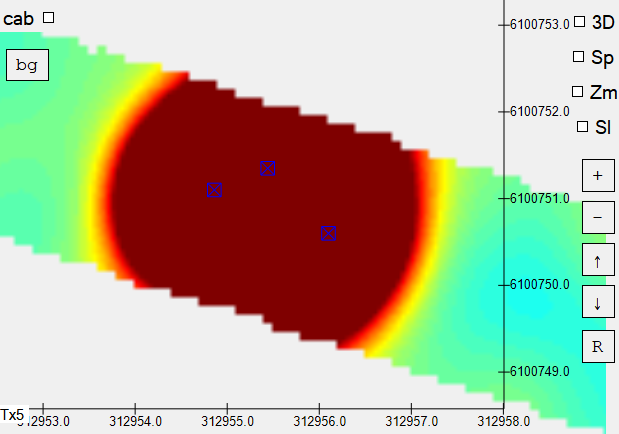
Now we can click on the Close and Set Seeds button to generate the synthetic data. Here is the result of our synthetic three source seeding.
The ground truth location of the seeded sources are colored in blue:
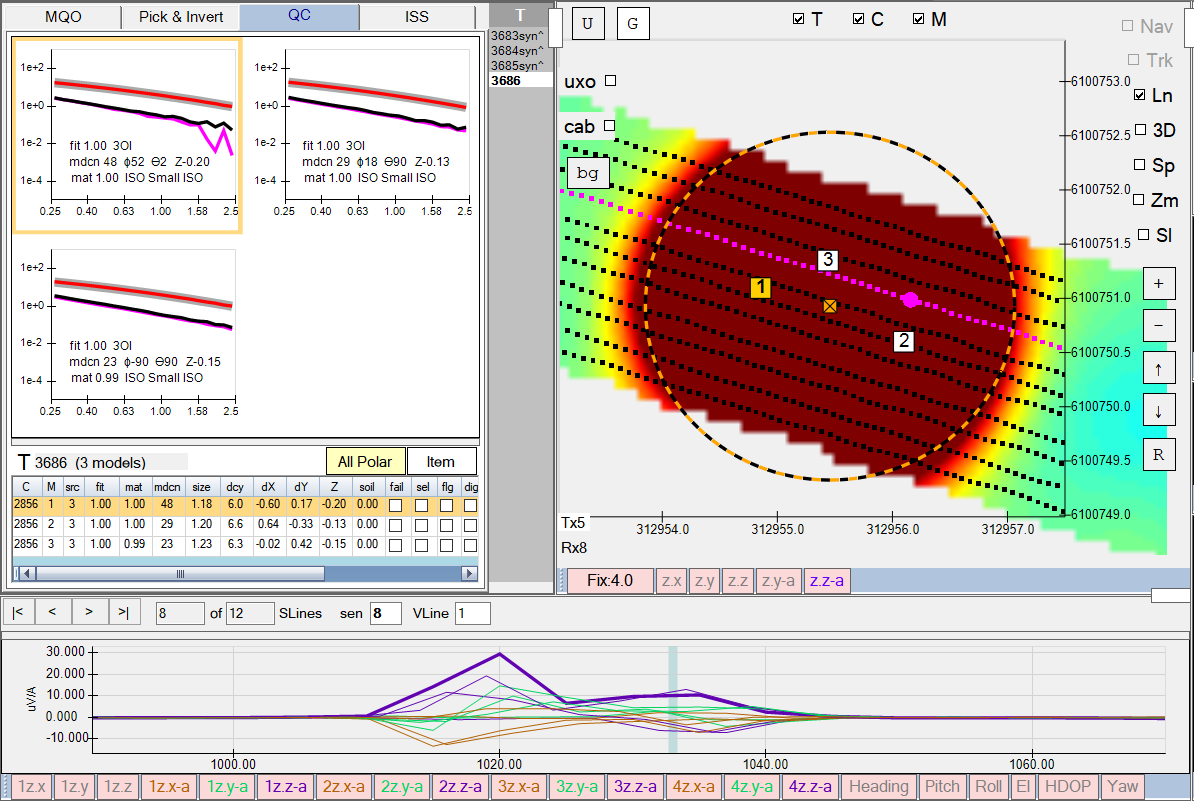
We can now invert the synthetic data to determine our accuracy in this three source scenario. Here are the results of a three object inversion (3OI). In this case the UT4-NATA system performs quite well, correctly locating all three sources very close to the ground truth locations, ground truth orientations, and library matches.
Here is another example of synthetic seeding, but this time we will use the UT4-CA Screener system. As we did previously, we can copy one of the IVS surveys to a SYNTH type and open it.
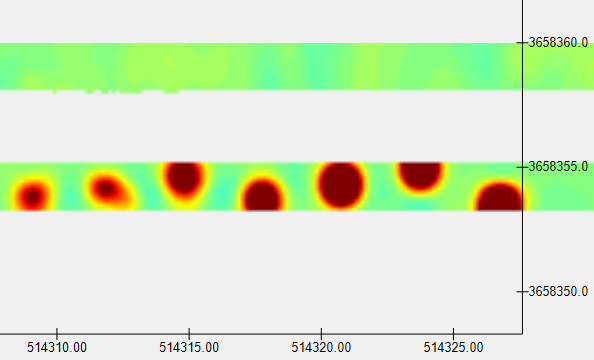
We can use the northern lane for our synthetic seeds:
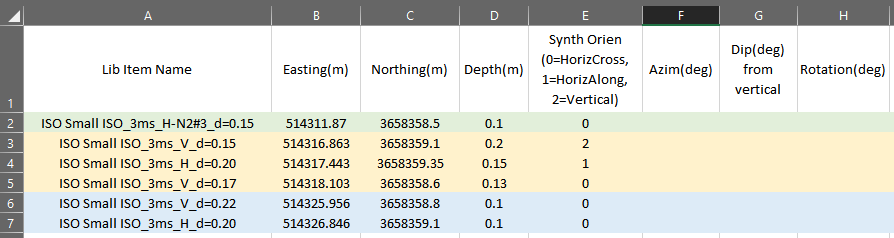
In our csv file we have configured a single source, a three source, and a two source seeding as shown here:
Here is a look at the data after generating the seeds:
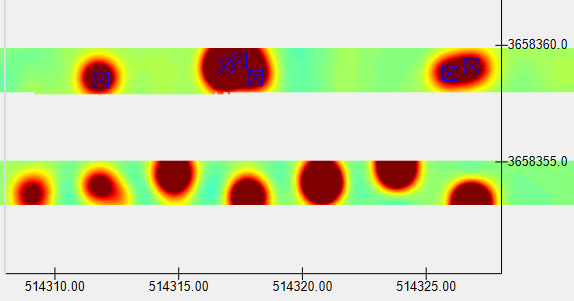
Here is the inversion result of the single source (West side), giving us good accuracy:
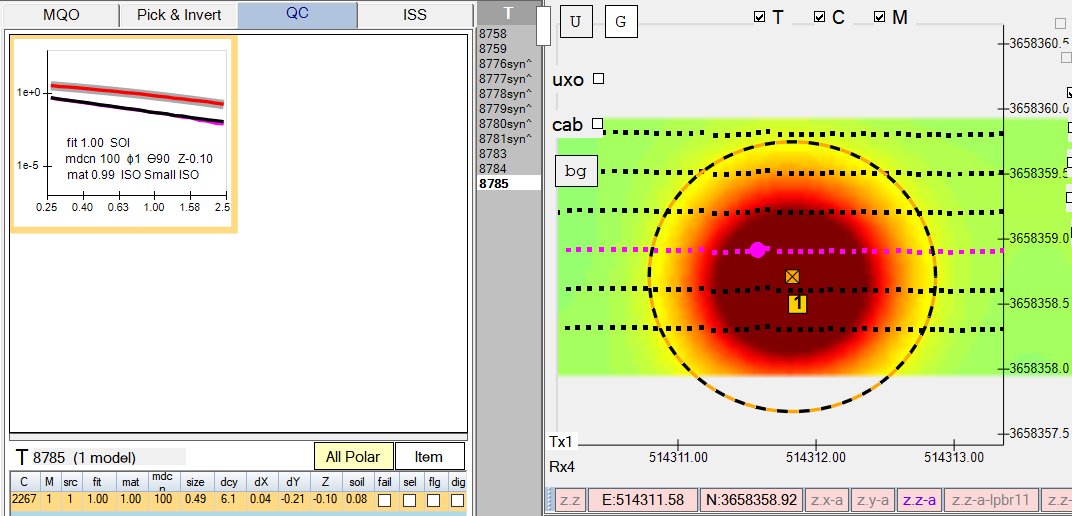
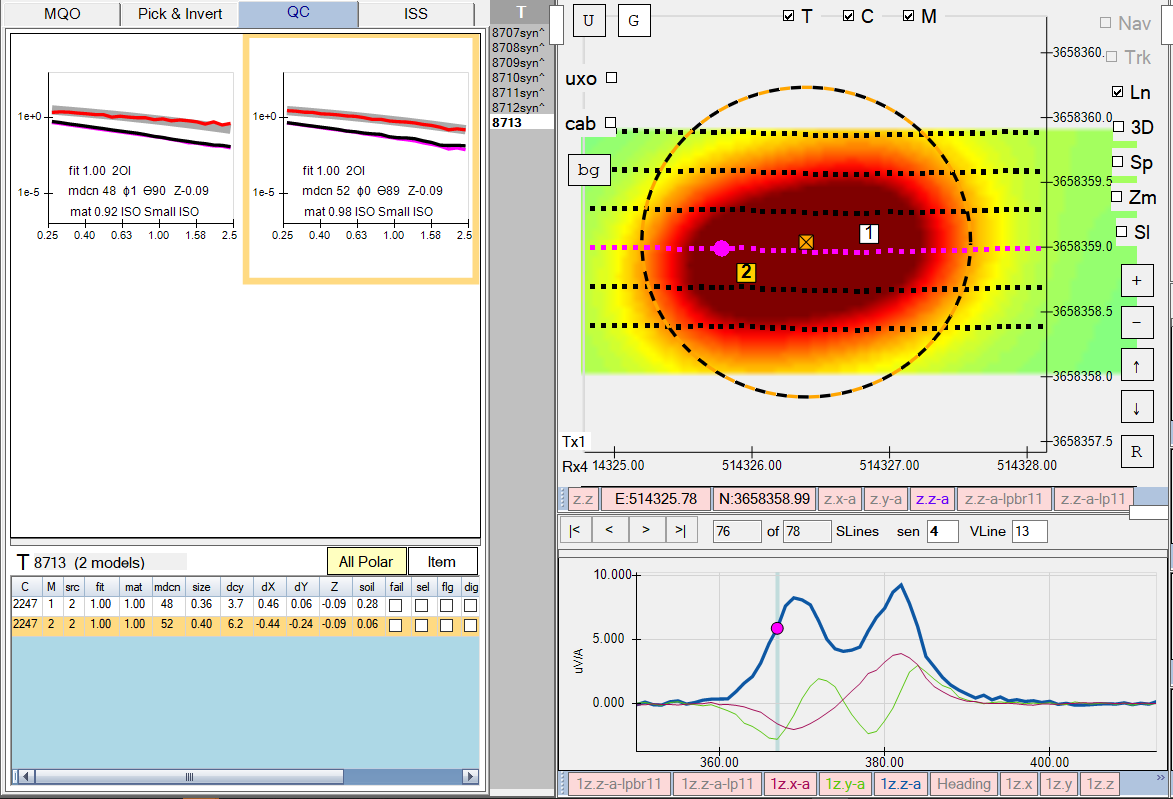
….and here is the inversion result of the two source seeding (East side), indicating both sources were correctly located in their ground truth horizontal cross-track orientations
Workflow for Synthetic Seeding Analysis
The following presents an example of synthetic seeding analysis used to assess the ability to recover a Small ISO at a project site.
Create the CSV file for specifying seed location and properties
- Define area of seeding. This can be done by using an existing coverage polygon.
- Generate a grid of seed locations. This can be performed in most popular GIS applications. The user can add attributes for the depth and orientation for each point feature. Then export the point layer to a CSV file.
- Format the CSV file for importing into BTField. Add a column for the library item name.
Create a new site for the seeding analysis
- Create a new site for the SYNTH surveys.
- Highlight all surveys you plan on seeding into and copy them to a SYNTH survey.
- Next highlight all the SYNTH surveys and move them to the SYNTH site created above.
Generate seed response and invert
- Import the seeding CSV into BTField, which generates the seed responses.
- Remove existing targets created from setting the seeds and run target picking.
- Run inverion
- ISS