Summary
This document describes how to perform standard threshold target picking using the Blakely Peak Detector Algorithm (Blakely, 1986).
Pre-requisites
Target picking
Configure the picking function
- Starting from the Pick & Invert tab.
- Open the Drag & Drop Functions menu button, f(x).
- From the Target Pick node, drag the Detect Targ function into the target picking flow.
- Select the New button to configure a target picker.
- Following the video below enter each piece of information.
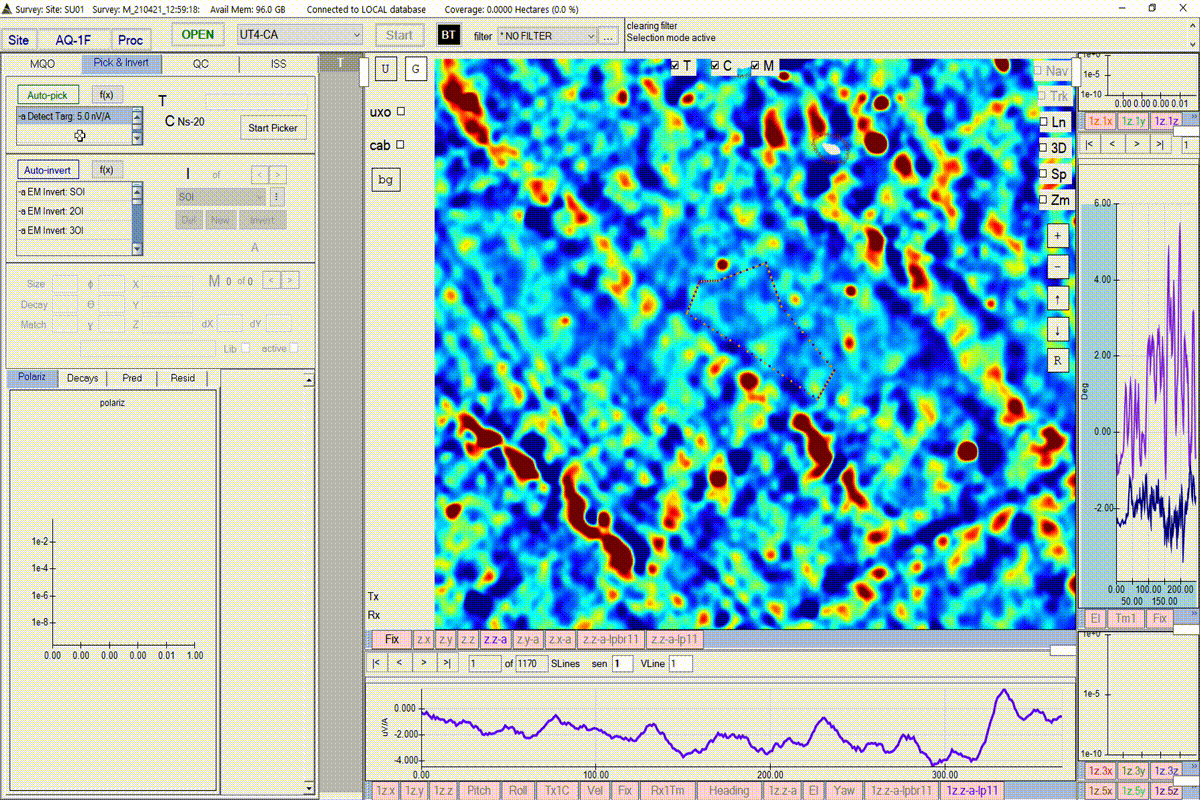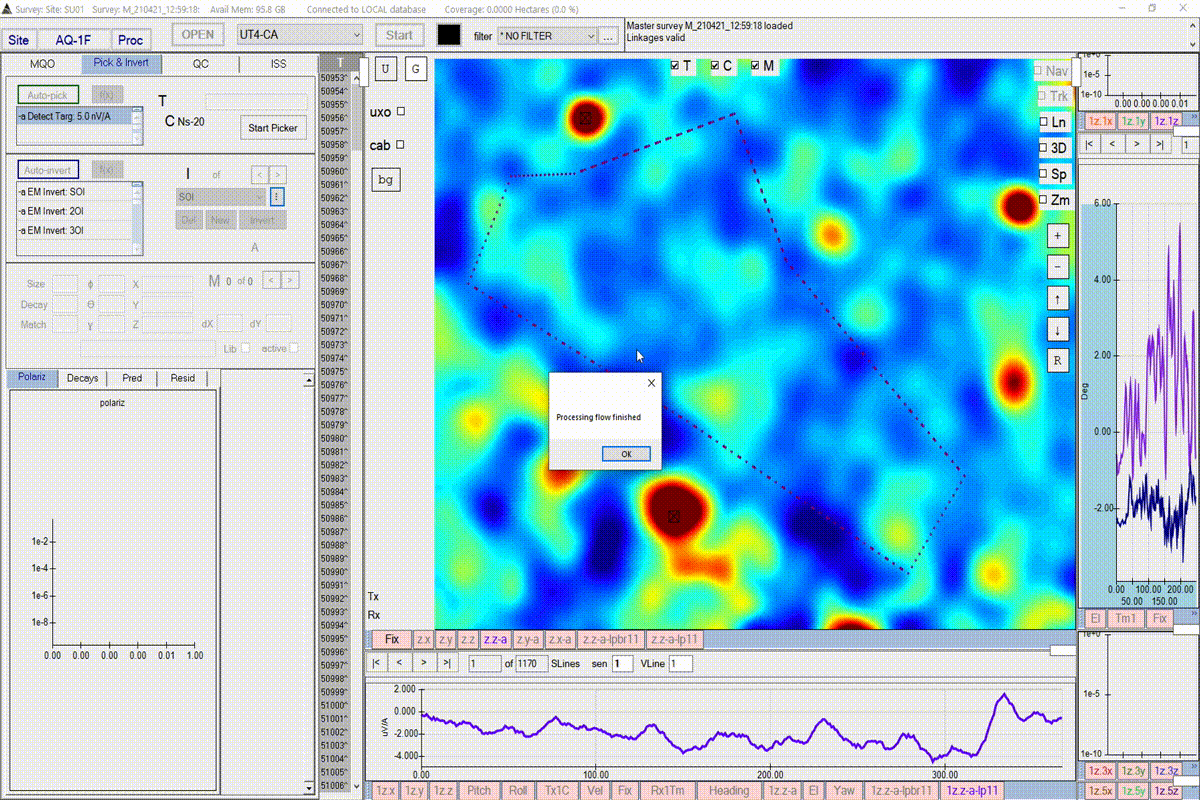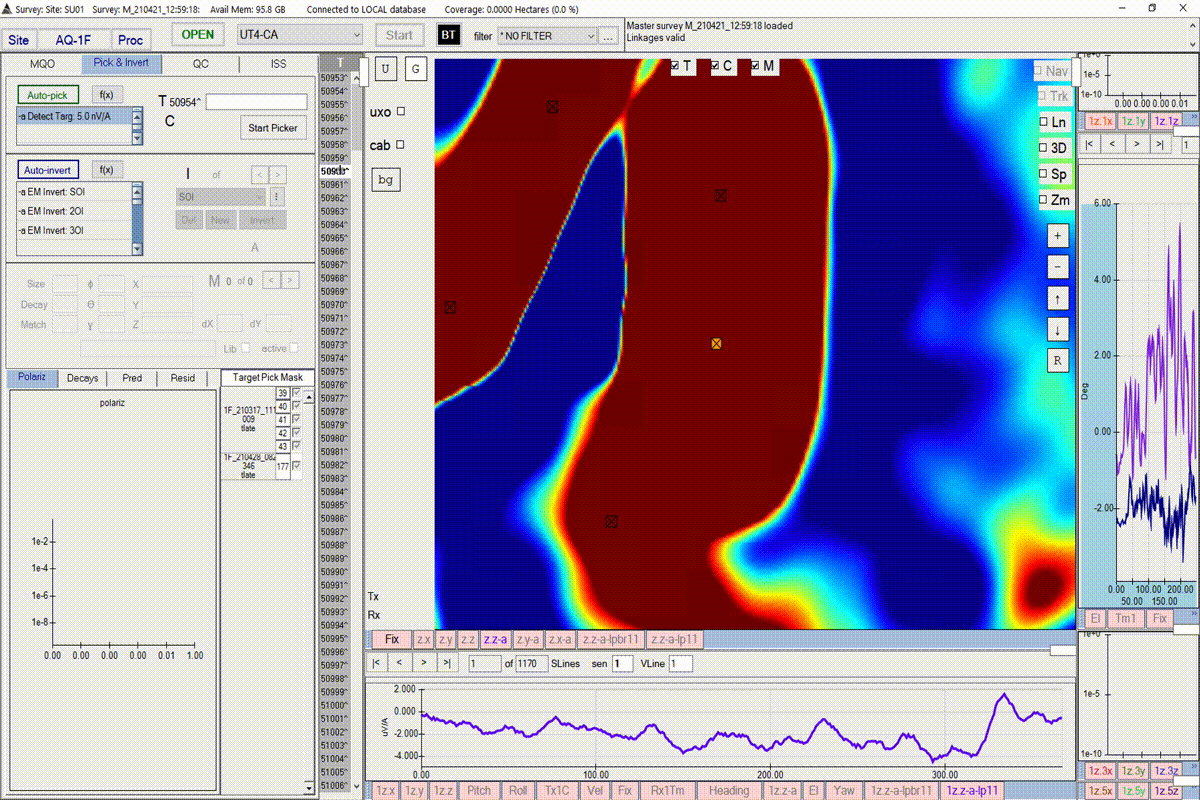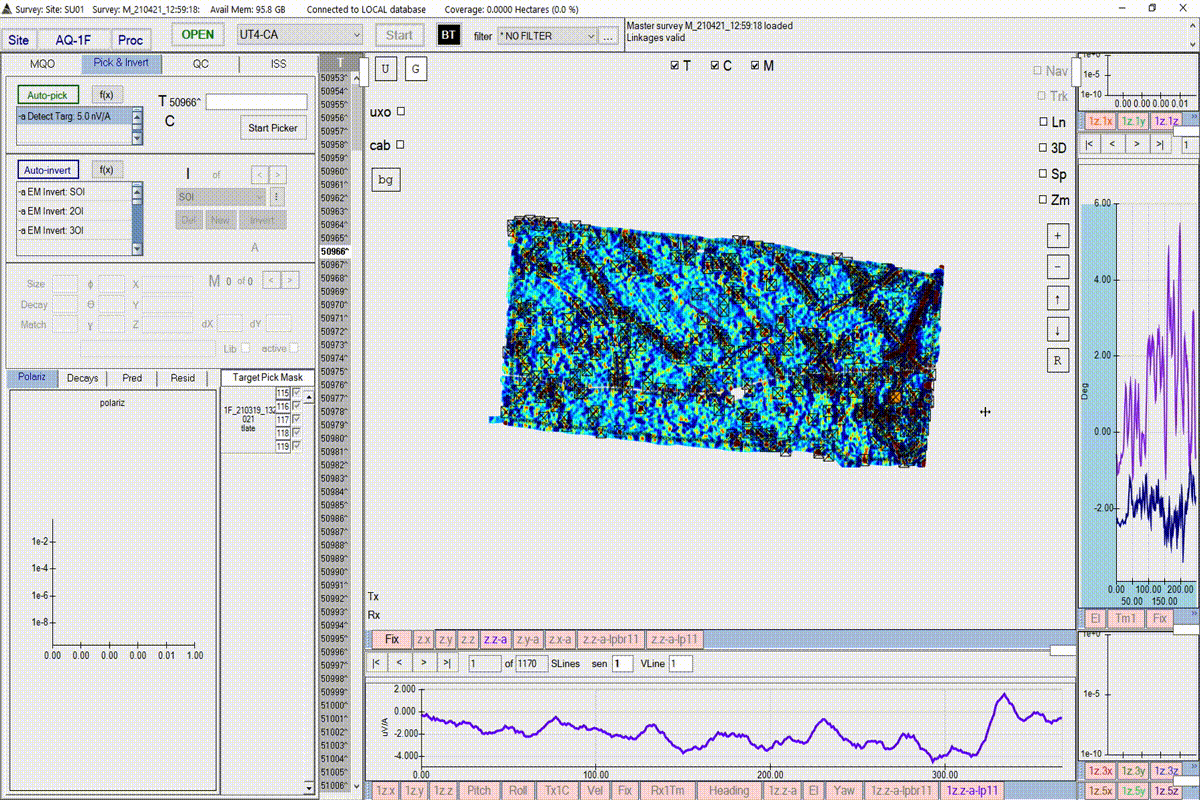
Create a noise polygon
BTField requires that the user creates a noise polygon before running a target picker. The user will be warned if the picking threshold is too close to the noise estimated from the noise polygon. Follow the steps in the video to create a noise polygon. Complete the polygon by pressing the return key.
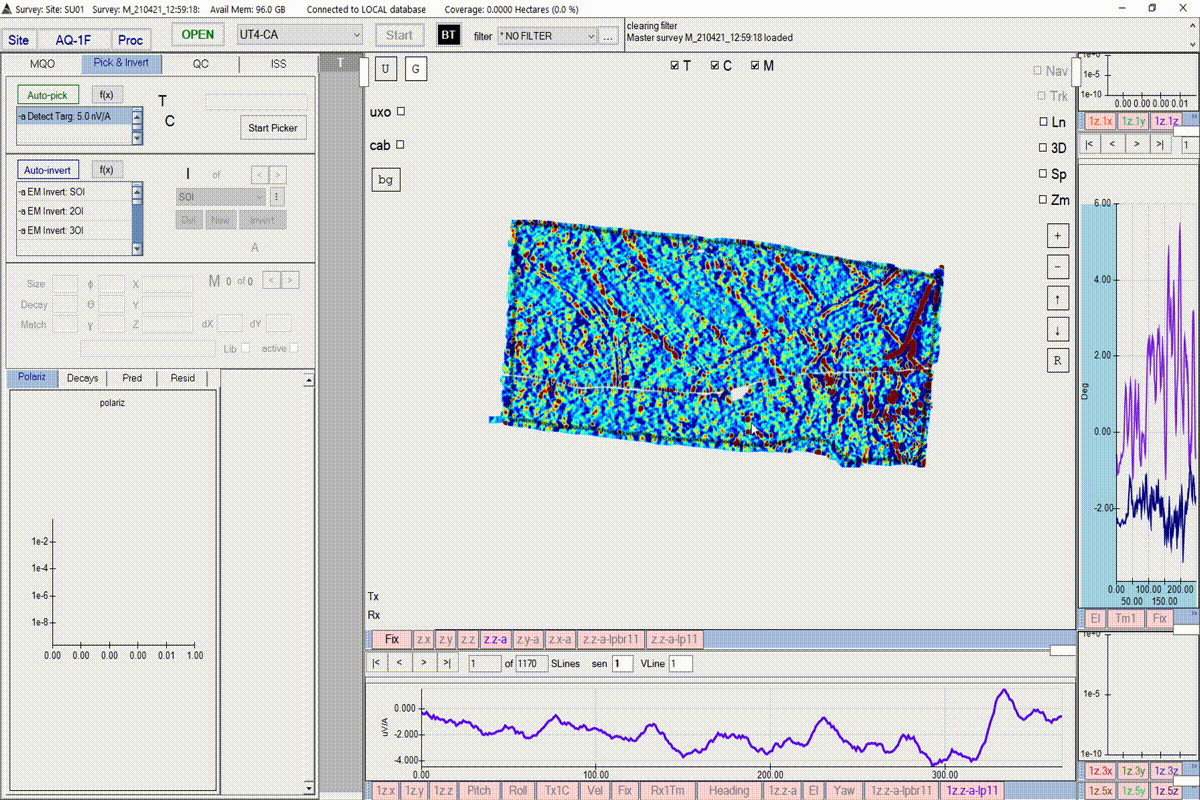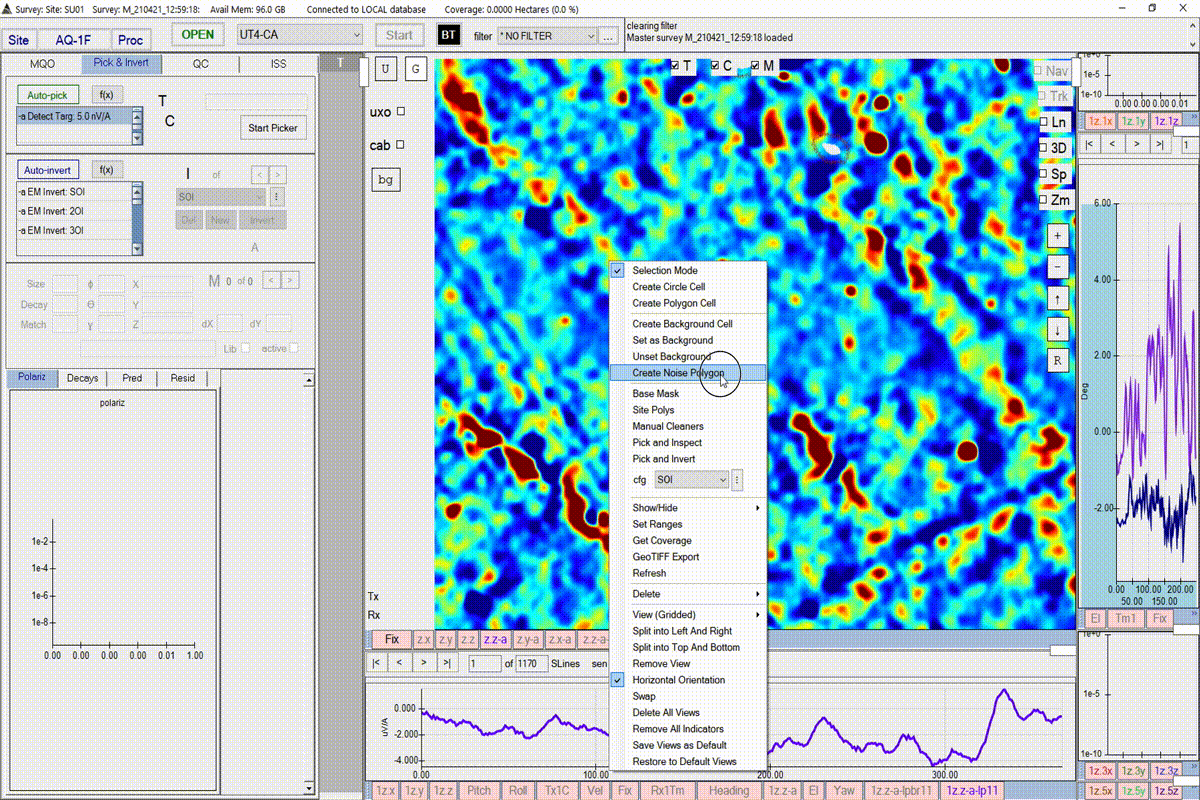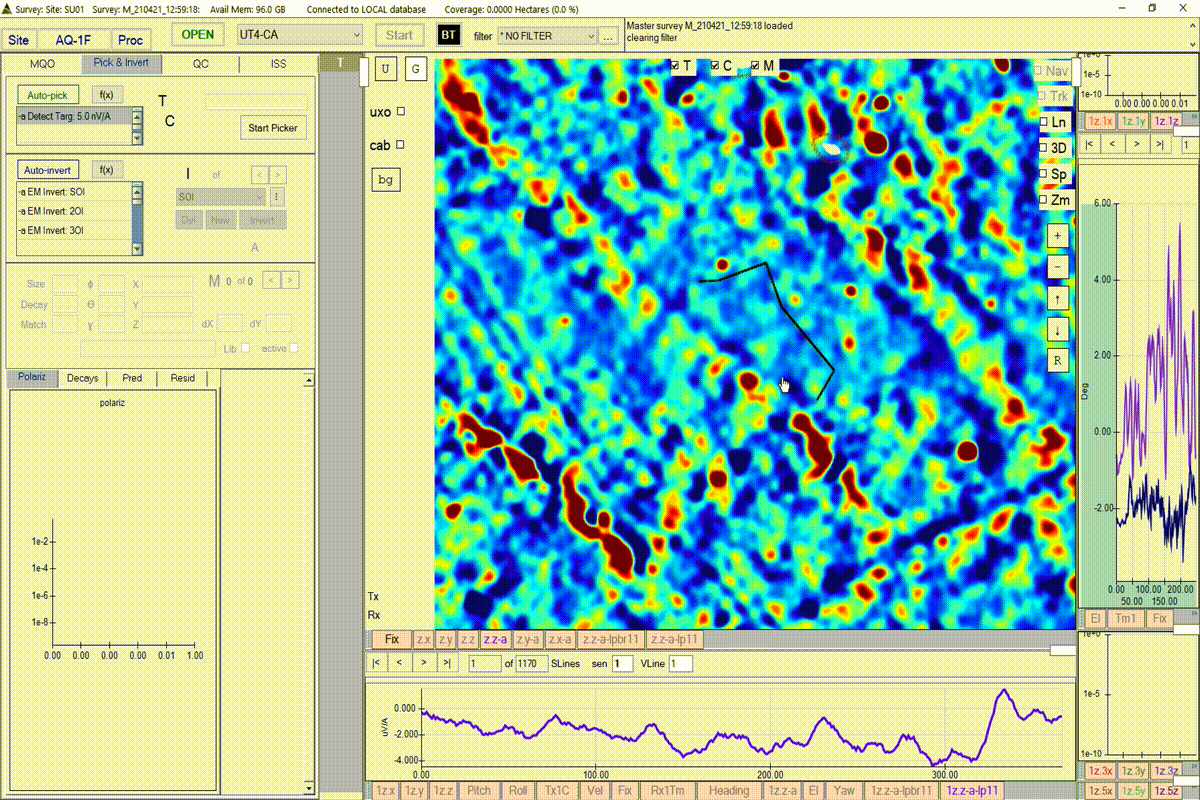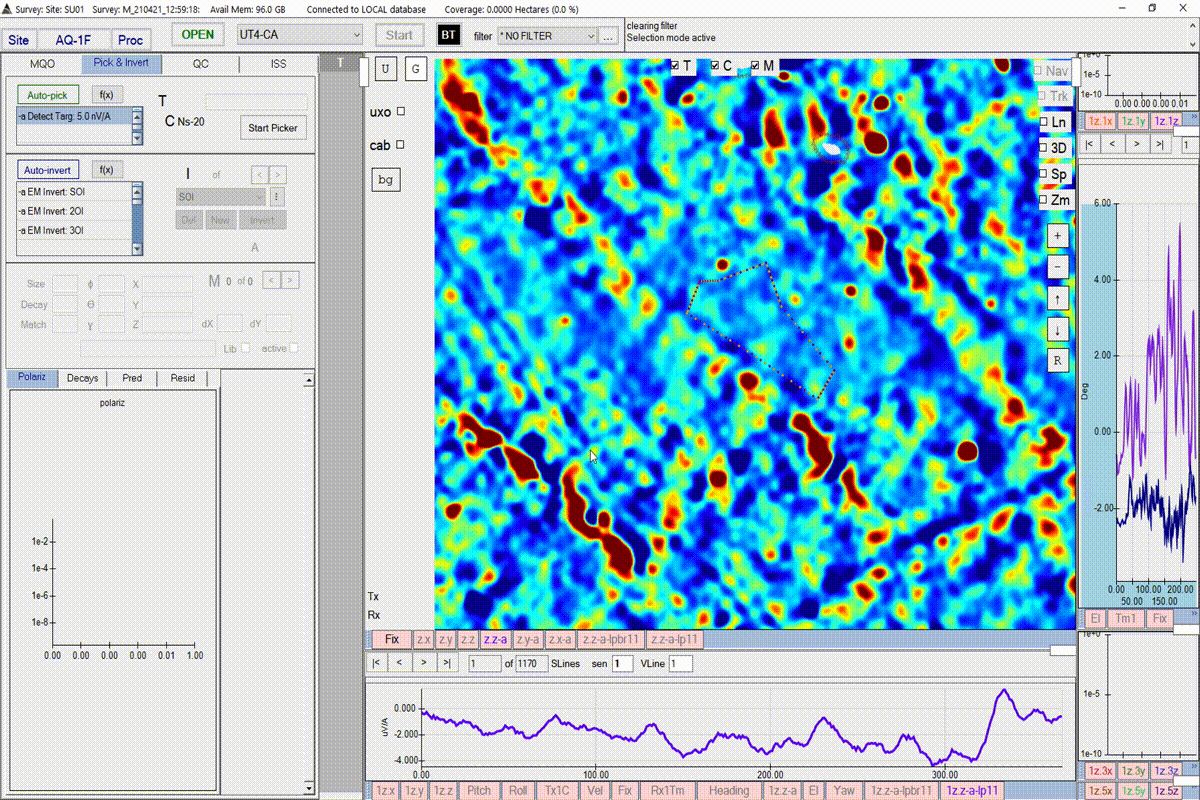
The user may also want to record the value of the noise within the noise polygon. This can be done by right-clicking on the polygon and selecting Copy Noise Values.
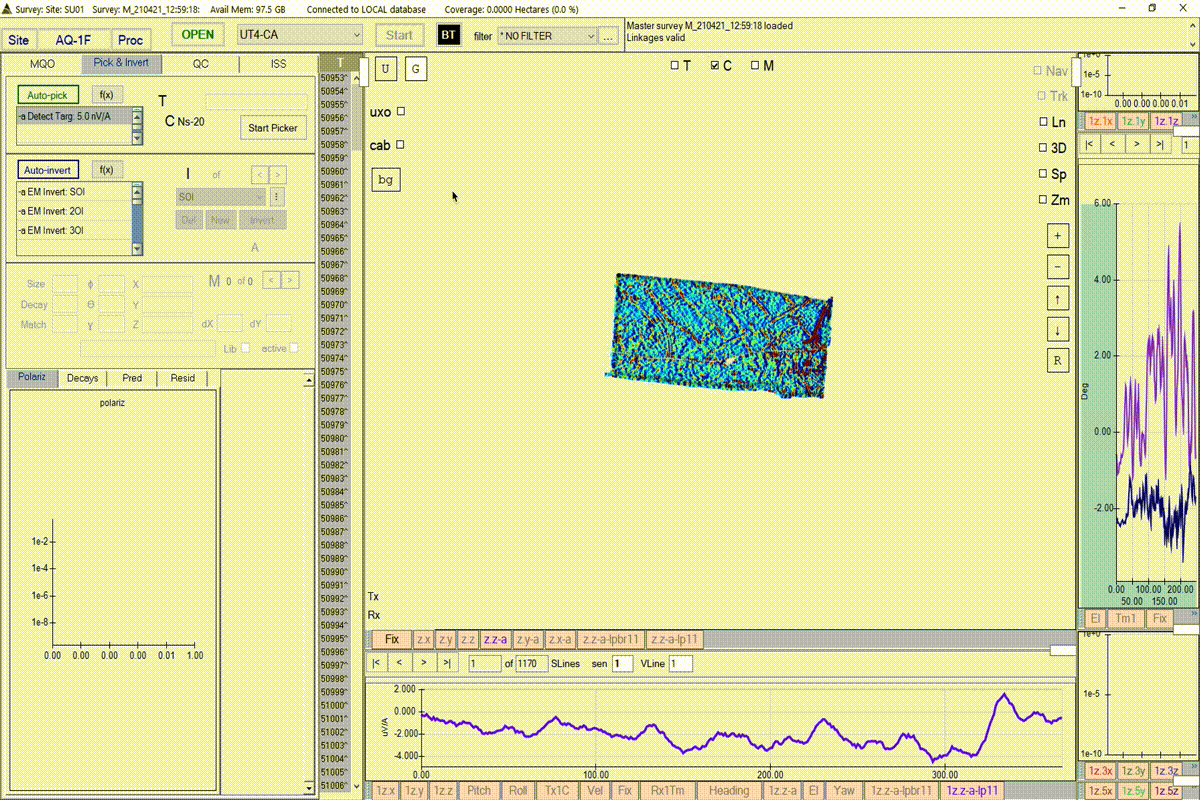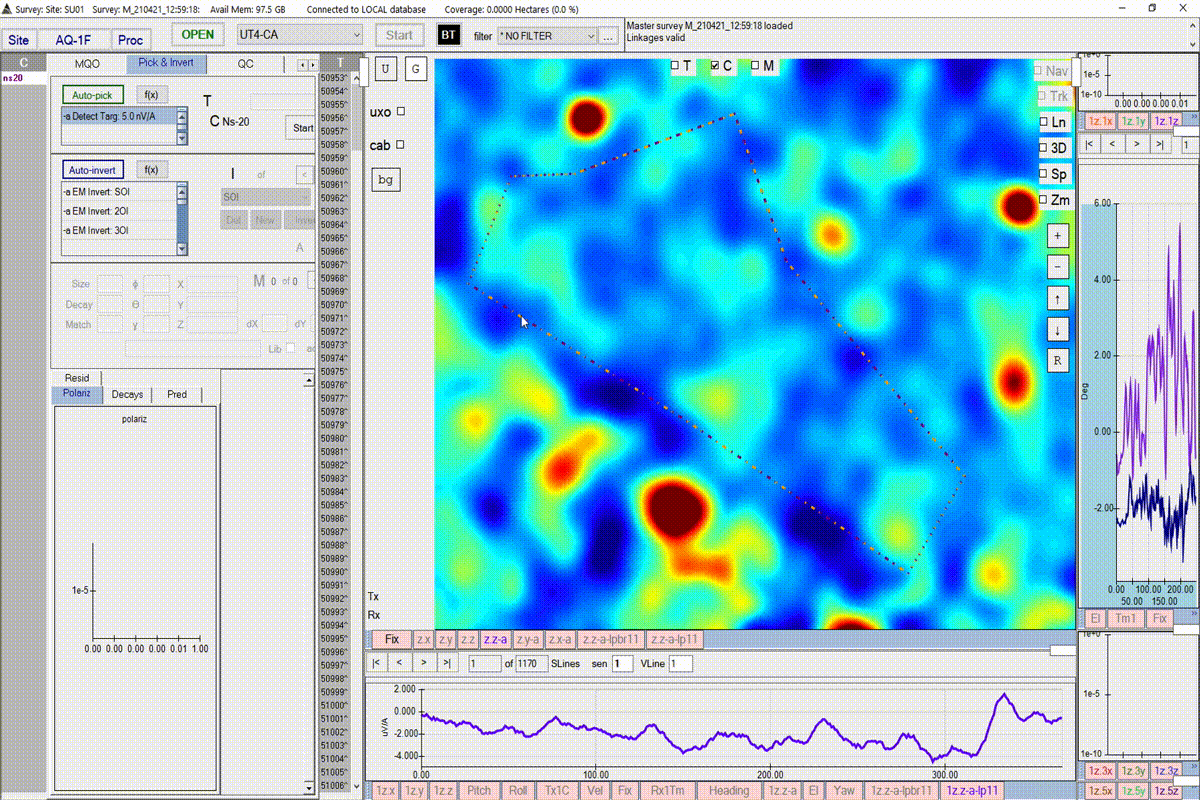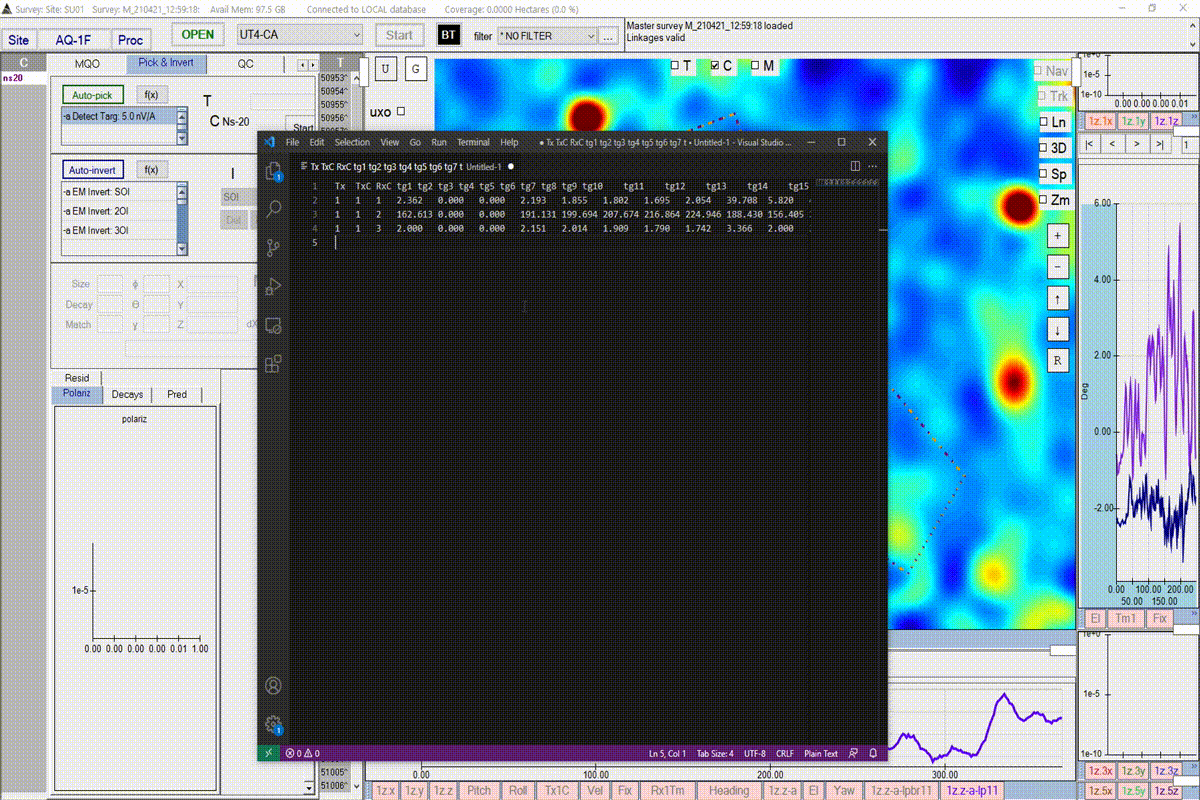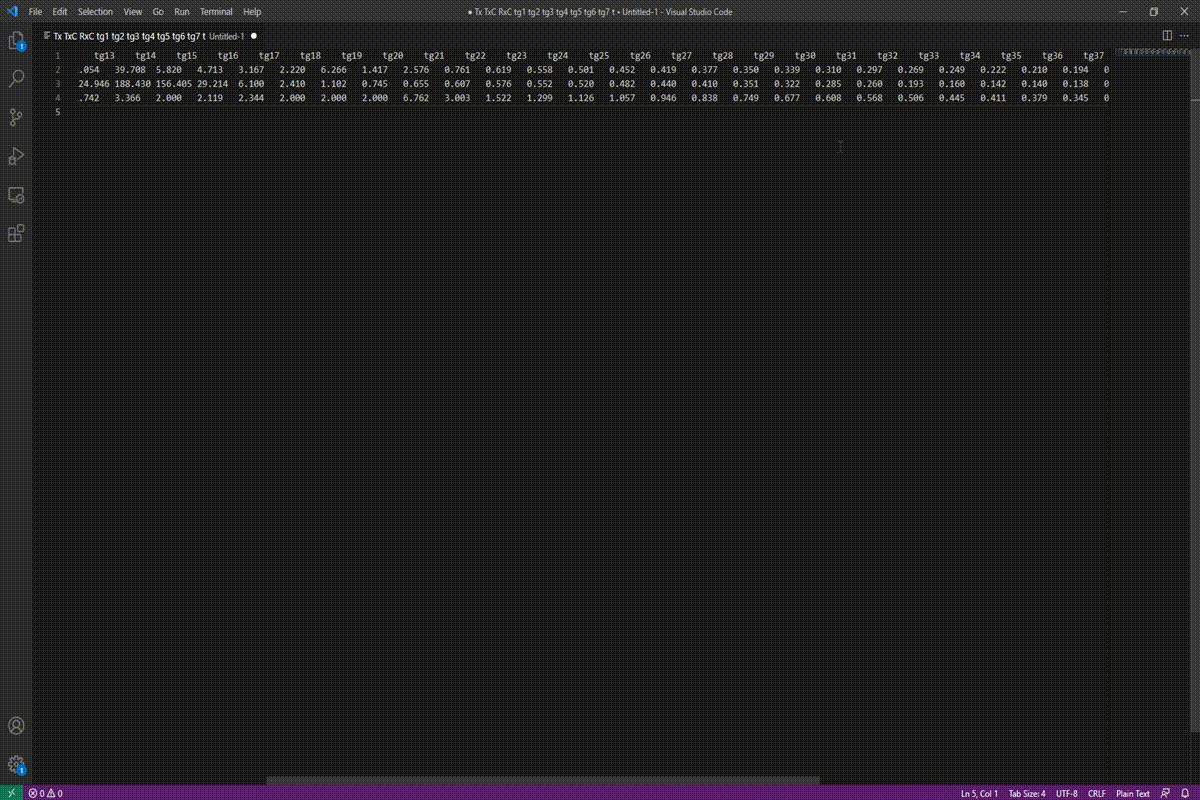
Run the picking function
Start the target picker by pressing the Auto-pick button. BTField may take a while to respond for datasets where many targets are found. Please wait till it’s finished. Note: the video below has had time clipped away while waiting for the taret picker to complete processing.
Parameter definitions
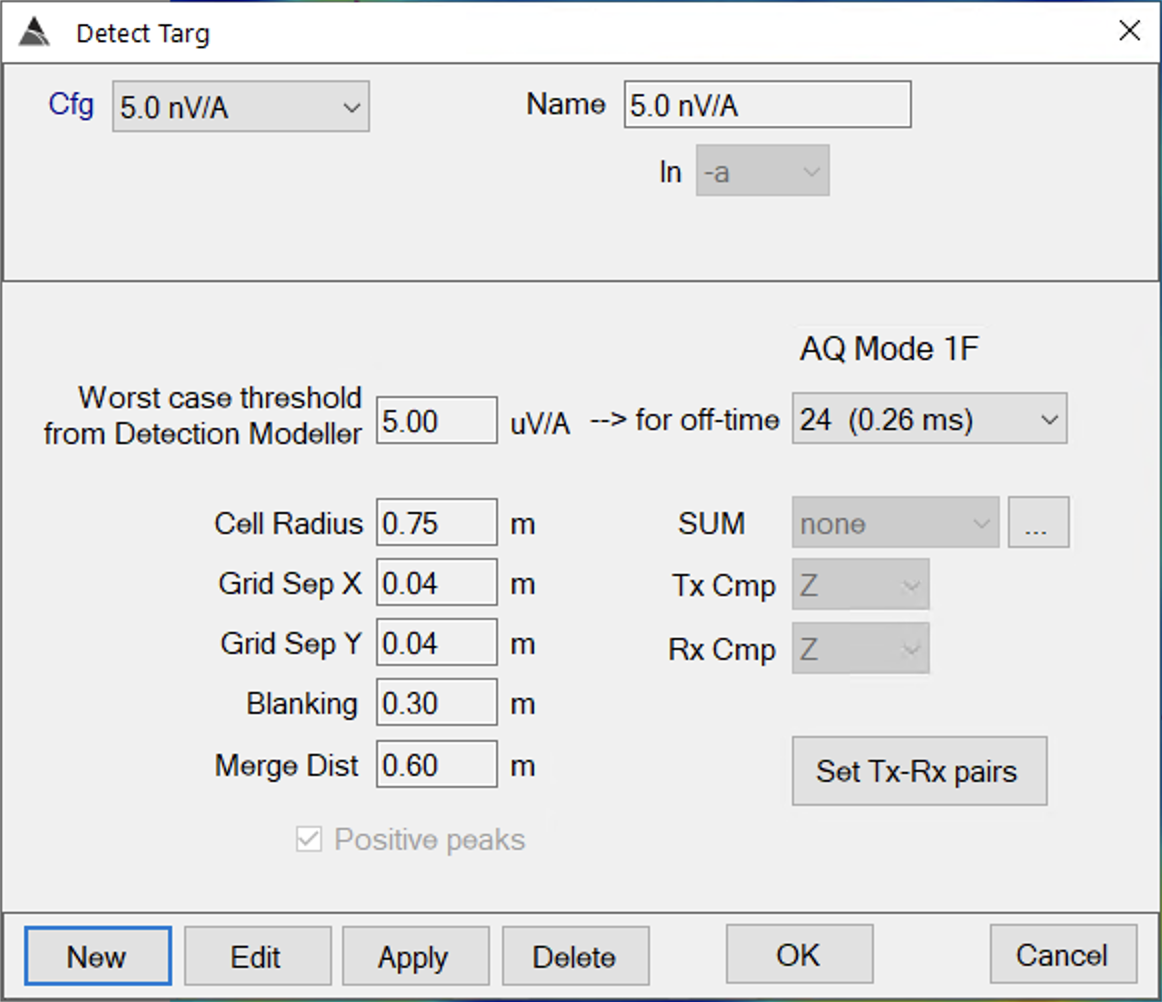
- Cfg: This shows the name of the configured picker. Each time you press New and save a new picker, it’s name will appear in this dropbox.
- Name: User may enter or edit the name of a configured picking function.
- ln: Select the data state to pick on. This is typically selected to be data state -a.
- Worst case threshold from Detection Modeller: This is the threshold at which to pick targets.
- Cell Radius: Search radius for any point that is a maximum within a circle of radius is selected as a pre-merge target.
- Grid Sep X: Grid spacing in the x-direction.
- Grid Sep Y: Grid spacing in the y-direction.
- Blanking: Distance of a grid node from a data point at which to assign a null value to the grid.
- Merge Dist: Minimum distance allowed for neighboring picks. Picks within this distance of a pick with greater amplitude will be removed.
- Positive peaks: Toggle to allow picking of both negative and positive peaks.
- for off-time: The time channel at which the threshold will be applied.
- SUM: For advanced configuration of summed and specialized target picking channels.
- Tx Cmp: Tx component to use.
- Rx Cmp: Rx component to use.
- Set Tx-Rx pairs: Allows user to select which Tx-Rx pairs will be used for target picking.
References
Blakely, R. J., and Simpson, R.W., 1986, Locating edges of source bodies from magnetic or gravity anomalies: Geophysics, v. 51, p. 1494-1498.